Apinae Apis
Cytogenetic data
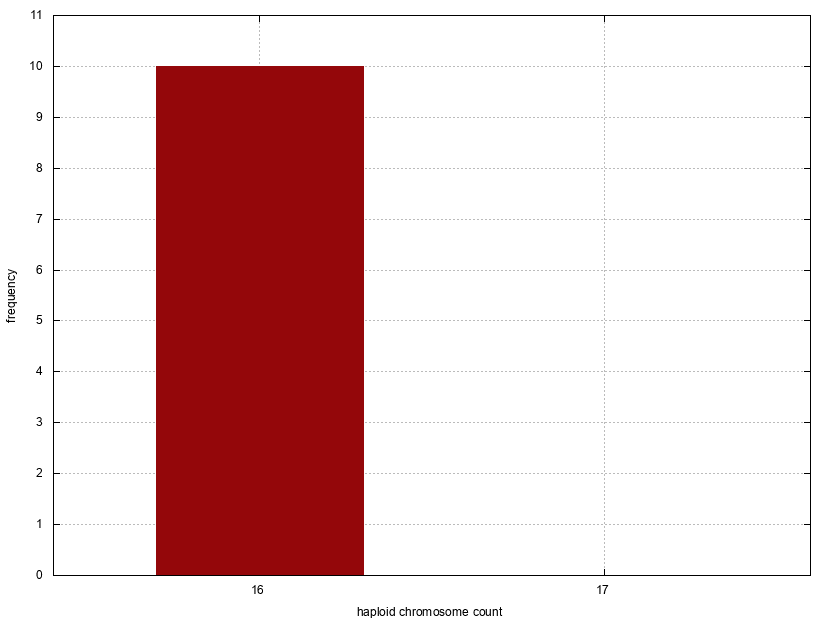
| Tribe | Species | Sample local | Country(ies) | Haploid(n) | Diploid(2n) | Karyotype | Notes | Genome size (pg) | Classic cytogenetic data | Molecular cytogenetic data | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apini | Apis cerana | Bangkok | Thailand | 0.19 | Jordan and Brosemer 1974 Ardila-Garcia et al. 2010 | ||||||
| Apini | Apis cerana | Machida, Tokyo | Japan | 16 | 32 | all metacentric or submetacentric | as Apis cerana japonica | C-banding; G-banding | Hoshiba et al. 1981 Hoshiba and Okada 1986 Hoshiba and Imai 1993 | ||
| Apini | Apis cerana | Mahabaleshwar | India | 16 | 32 | k= 4metacentric + 4submetacentric + 8subtelocentric | as Apis indica | Deodikar et al. 1959 | |||
| Apini | Apis cerana | University of Peradeniya | Sri Lanka | 16 | Fahrenhorst 1977 | ||||||
| Apini | Apis dorsata | University of Peradeniya | Sri Lanka | 16 | Fahrenhorst 1977 | ||||||
| Apini | Apis florea | University of Peradeniya | Sri Lanka | 16 | Fahrenhorst 1977 | ||||||
| Apini | Apis mellifera | University of Peradeniya | Sri Lanka | 16 | Fahrenhorst 1977 | ||||||
| Apini | Apis mellifera | Itabashi-ku, Tokyo | Japan | 16 | 32 | all metacentric or submetacentric | as Apis mellifera ligustica | C-banding; G-banding | Hoshiba and Kusanagi 1978 Hoshiba 1984a Hoshiba 1984b Hoshiba and Okada 1986 Hoshiba and Imai 1993 | ||
| Apini | Apis mellifera | Guelph, Ontario | Canada | 16 | 32 | 0.24 | HoneybeeGenomeSequencingConsortium 2006 Ardila-Garcia et al. 2010 | ||||
| Apini | Apis mellifera | Locality not specified | Germany | 16 | FISH (ribosomal probe, TTAGG probe) | Beye and Moritz 1993 Sahara et al. 1999 | |||||
| Apini | Apis mellifera | Banat, Timok and Syenichko–Peshterski | Serbia | 32 | as Apis mellifera carnica | G-banding | Stanimirovic et al. 2005 |
Chromosome classification: Levan et al. (1964): metacentric (m), submetacentric (sm), subtelocentric (st), or acrocentric (a). Imai (1991): metacentric (M) or acrocentric (A), with a variety of forms depending on the position of the heterochromatin on the karyotype.
You can download this data as csv.
Histogram
Bibliography
Ardila-Garcia, A.M., Umphrey, G.J., Gregory, T.R. An expansion of the genome size dataset for the insect order Hymenoptera, with a first test of parasitism and eusociality as possible constraints. Insect Molecular Biology, 19 : pp 337-346. 2010. DOI: [10.1111/j.1365-2583.2010.00992.x https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583.2010.00992.x]
Hoshiba, H., Okada, I. G-Banding analyses of male chromosomes in Apis cerana and A. mellifera ligustica. Apidologie, 17 : pp 101-106. 1986. DOI: [10.1051/apido:19860203 https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:19860203]
Fahrenhorst, H. Nachweis ubereinstimmender Chromosomen-Zahlen (n = 16) bei allen 4 Apis-Arten. Apidologie, 8 : pp 89-100. 1977. DOI: [10.1051/apido:19770107 https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:19770107]
Hoshiba, H., Kusanagi, A. Karyological study of honeybee. Journal of Apicultural Research, 17 : pp 105-109. 1978. DOI: [10.1080/00218839.1978.11099913 https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.1978.11099913]
Sahara, K., Marec, F., Traut, W. TTAGG telomeric repeats in chromosomes of some insects and other arthropods. Chromosome Research, 7 : pp 449-460. 1999. DOI: [10.1023/A:1009297729547 https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009297729547]
Beye, M., Moritz, R.F.A. In situ hybridization of rDNA on chromosomes of the honeybee, Apis mellifera L.. Experientia, 49 : pp 337-338. 1993. DOI: [10.1007/BF01923416 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01923416]
Hoshiba, H., Okada, I., Kusanagi, A. The diploid drone of Apis cerana japonica and its chromosomes. Journal of Apicultural Research, 20 : pp 143-147. 1981. DOI: [10.1080/00218839.1981.11100488 https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.1981.11100488]
Jordan J.R., Brosemer R.W. Characterization of DNA from three bee species. Journal of Insect Physiology, 20 : pp 25132520. 1974. DOI: [10.1016/0022-1910(74)90035-3 https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(74)90035-3]
Hoshiba, H., Imai, H. Chromosome evolution of bees and wasps (Hymenoptera, Apocrita) on the basis of C-banding pattern analyses. Japanese Journal of Entomology, 61 : pp 465-492. 1993
Hoshiba, H. Karyotype and banding analyses on haploid males of the honey bee (Apis mellifera). Proceedings of the Japan Academy Series B, 60 : pp 122-124. 1984a. DOI: [10.2183/pjab.60.122 https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.60.122]
Honeybee Genome Sequencing Consortium. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nature, 443 : pp 931-949. 2006. DOI: [10.1038/nature05260 https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05260]
Stanimirovic, Z., Stevanovic, J., Andjelkovic, M. Chromosomal diversity in Apis mellifera carnica from Serbia. Apidologie, 36 : pp 31â42. 2005. DOI: [10.1051/apido:2004067 https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:2004067]
Hoshiba, H. The C-banding analysis of the diploid male and female honeybee (Apis mellifera). Proceedings of the Japan Academy Series B, 60 : pp 238-240. 1984b. DOI: [10.2183/pjab.60.238 https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.60.238]
Deodikar, G.B., Thakar, C.V., Shah, P.N. Cyto-genetic studies in Indian honeybees. I. Somatic chromosome complement in Apis indica and its bearing on evolution and phylogeny. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences Section B, 49 : pp 194-206. 1959
